Interesting article from Matériautech d’Allizé-Plasturgie
(original article can be viewed here: https://www.allize-plasturgie.org/fr/innovation-matieres-et-process/essais-matieres-avec-la-technologie-roctool )
Material tests with Roctool technology
To address the current limitations of current thermoregulation processes, Roctool has developed a technology that can replace it: 3iTech™. In partnership Matériautech d’Allizé-Plasturgie and various teams from SMP, Kistler, GMV Eschmann & Cadflow, several material injection tests were carried out.
As part of a study with recycled polycarbonate (rPC) several tests were carried out with the GEM High Temperature demonstrator mold designed with Roctool. The design of this mold was specially designed to evaluate the performance of this Heat & Cool technology according to various criteria.
Heat & Cool
The 3iTech™ process allows thermal cycling of injection tools. The technology used is induction, via the integration of inductor networks located in the molds. This technology covers a wide range of temperatures (50°C to 400°C) in seconds. Cooling is provided by integrated water channels situated behind the inductor network. The mold temperature can be controlled during the injection phase, ensuring the stability of the process while improving the quality of the injected parts.
Indeed, we evaluate the filling of the injected part on 3 thickness levels (2.5mm, 1.5mm & 1mm) the weld lines elimination and finally improved surface quality with a laser texture and polished mirror surface.
Studies carried out with two pressure sensors
The mold is equipped with two Kistler mold cavity pressure sensors, one at the beginning of the filling and the other one at the filling end. Two Roctool generators equip the tool, one for the mobile part and the other for the fixed part.
The heating of the two parts of the mold significantly modifies the flow of the material, imposing a drop in the injection speed and limiting the maximum temperature of the cavity to 135°C in order to avoid any material damage.
Once the different injection parameters were adjusted with Roctool, the injection heating was deactivated while retaining the injection parameters used previously with a tool regulation temperature of 80°C.
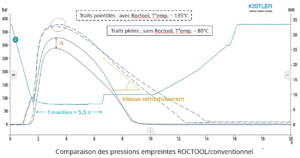
The injection time remains the same at 1.53 secs. which is consistent as we use an electric injection press. On the resulting parameters recorded on the press, we observe an increase of 12% of the switching pressure which goes from 830 bars with induction heating to 930 bars in conventional. Simultaneously, the cavity pressure decreases in conventional mode during the maintenance / cooling phases (cavity pressure curves recorded and plotted on the attached graph). The holding pressure applied is 600 bars in conventional and with Roctool technology. The pressure difference between the beginning and the end of filling the cavity is increased from 12 bars for a cavity temperature of 135°C to 41 bars for a cavity at 80°C. This results in a congealing of the conventional materials resulting in poor pressure distribution and therefore an increase in internal stresses in the injected part.
The amount of material injected, however, remains the same since the mass of the parts has not changed (15.31g and 15.34g). This observation makes it possible to note that if one positions oneself on an equivalent quality of densification, the holding pressure could be reduced by a few tens of bars by using induction to superimpose the imprint pressure curves, which will have the effect of lowering the mass injected.
The slope of the pressure curve at the end of filling indicates a cooling rate which is far greater with Roctool. This is due to the use of a thermoregulator with a flow rate of 25 l / min against a recommended flow rate of 100 l / min, a flow rate which would have made it possible to achieve an efficient cooling time. It is shown here that the regulation flow impacts the cooling rate more than the temperature of the fluid.
Significant improvement in the appearance of parts.
In terms of the injected parts appearance, Roctool eliminates weld lines and cold drop traces on the surface near the injection point. The replication of the laser texture is finer with an improvement in the gloss on the polished area, thereby modifying the rendering.

Left part: Gem produced with conventional molding;
Right part: Gem produced with Roctool technology
The results are even more convincing with high performance materials such as PPSU and PEI with fibers. In fact, for PEI with glass fibers, the fibers are present on the surface with conventional molding at 160°C, and are eliminated with Roctool technology at 220°C. This gives a smooth and shiny surface.
In terms of dimensional rendering, we submitted to GOM, a company offering high-precision 3D industrial metrology solutions, two Gems molded in PPSU under the same injection conditions but at two different mold temperatures: conventional at 160°C and induction at 220°C. On the Gem injected at 220°C, we noticed a lower average thickness of 0.02 mm in the areas of thicknesses 1.5 and 1 mm and dimensions in width and length of work larger than 0.07 mm. These measured differences between the two injection technologies compared are small, the material used having an amorphous structure, but nevertheless reflect a trend which would need to be validated with a material of semi-crystalline structure.
Other comparative studies will soon be carried out on other high performance materials such as LCP, PPS and specialty PA.
Matériautech d’Allizé-Plasturgie
Matériautech supports you in all your material transformation issues and helps you identify the appropriate processes.


